DMSP/OLS夜间灯光遥感影像
DMSP/OLS夜间灯光遥感影像为从太空监测人类活动提供了一个非常方便的手段,应用十分广泛。但是由于多种因素的影响,其时间序列的连续性很差,严重影响了对人类活动的动态监测,因此对其进行订正一直是一个热点和难点。我们提出了一个鲁棒算法,规避了传统方法人为选择校准场的主观影响,成功生成了时间连续的夜间灯光序列,为动态监测人类活动提供了方便。
Problem: DMSP/OLS nighttime light data has been widely used to monitor human activities from space. However, data acquired from different sensors are not directly comparable (Fig. 1), due to a number of factors. Thus, change analysis with this data source is limited.
Research goals: 1) designing a robust method to calibrate DMSP/OLS nighttime light time series; 2) generating a new time series with this method; 3) evaluating its performance.
Methodology: The densest part of the scatterplot between the reference image and a target image forms a ridgeline that represents the majority of lit pixels (Fig.2a). Data points selected along the ridgeline are then used to build a linear regression model for calibrating the target image (Fig.2b).
Results and conclusions:
1. Visual (Fig. 3) and quantitative assessment results show that the RSR method can successfully generate a consistent nighttime light time series from DMSP/OLS data.
2. The RSR method avoids subjective selection of pseudo-invariant features on ground and used all lit pixels to develop calibrating models, thus it is more robust than existing methods. It further reduces computation burden to build models.
3. The newly generated nighttime light time series has the potential to study human activities at night over time.
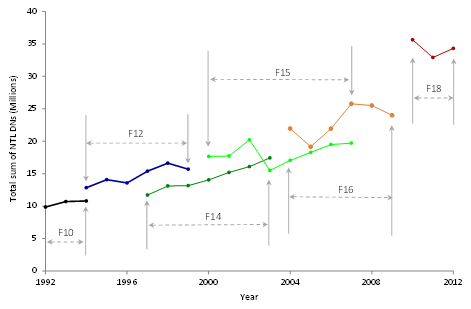
Fig. 1. DMSP/OLS nighttime light time series of Beijing, China. Large gaps can be easily observed among data segments from different sensors.
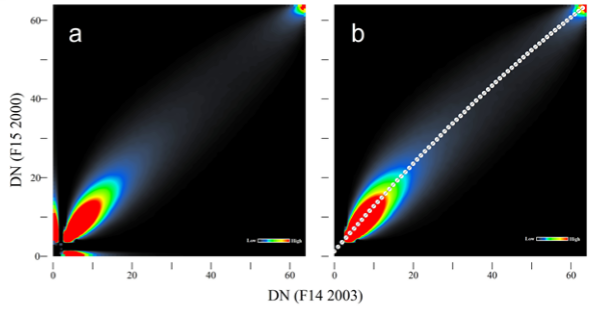
Fig. 2. The proposed Ridgeline Sampling and Regression (RSR) method.
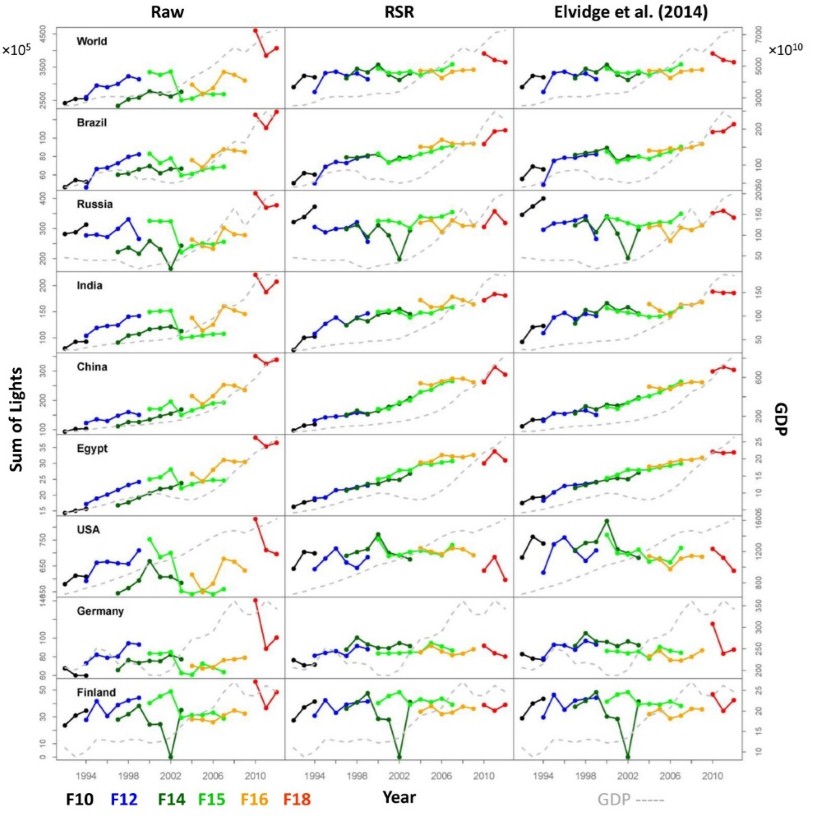
Fig. 3. Raw and calibrated DMSP/OLS nighttime light time series of selected regions worldwide.
